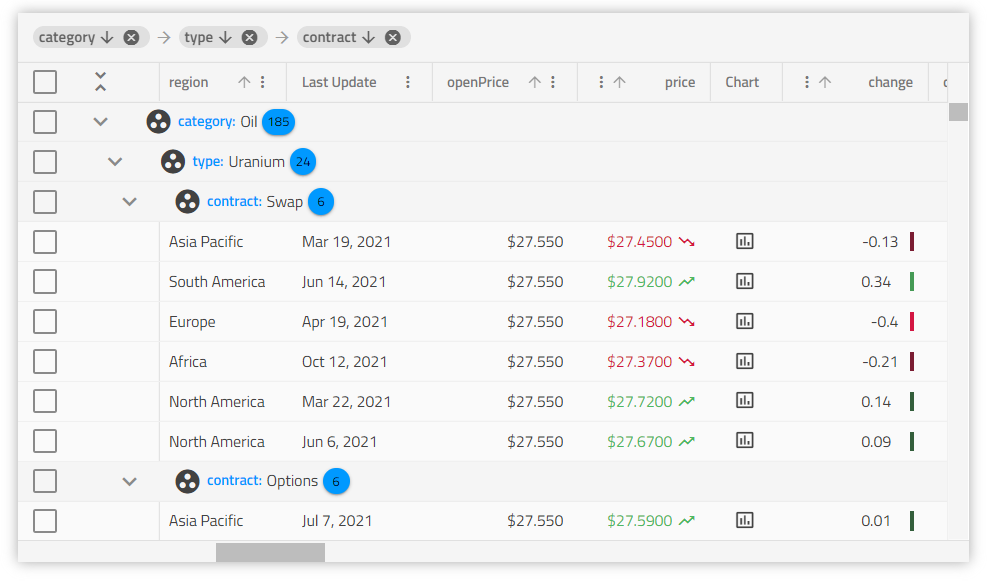
Visão geral e configuração do Web Components Grid
Web Components Data Grid Example
Neste exemplo de Ignite UI for Web Components Grid, você pode ver como os usuários podem fazer filtragem básica e no estilo do Excel, classificação de dados em tempo real e usar resumos de grade, bem como modelos de célula. A demonstração também inclui um conjunto de paginação para exibir 10 itens por página.
Getting Started with Web Components Data Grid
Dependencies
Para começar com o Web Components Data Grid, primeiro você precisa instalar oigniteui-webcomponents-grids pacote.
npm install --save igniteui-webcomponents-grids
Você também precisa incluir a seguinte importação para usar a grade:
import 'igniteui-webcomponents-grids/grids/combined.js';
Os estilos correspondentes também devem ser referenciados. Você pode escolher a opção clara ou escura para um dos temas e, com base na configuração do seu projeto, importá-lo:
import 'igniteui-webcomponents-grids/grids/themes/light/bootstrap.css';
Ou para vinculá-lo:
<link rel='stylesheet' href='node_modules/igniteui-webcomponents-grids/grids/themes/light/bootstrap.css'>
Para obter mais detalhes sobre como personalizar a aparência da grade, você pode dar uma olhada na seção de estilo.
Usage
Agora que temos os pacotes de grade importados, vamos começar com a configuração básica e vincular aos dados locais:
<igc-grid id="grid1" auto-generate="true"></igc-grid>
constructor() {
let grid1 = document.getElementById("grid1") as IgcGridComponent;
grid1.data = data;
}
Aid propriedade é um valor de cadeia e é o identificador único da grade, que será gerado automaticamente se não for fornecido, enquantodata vincula a grade, neste caso, a dados locais.
AautoGenerate propriedade orienta a grade a gerar automaticamente os componentes daIgcColumnComponent grade com base nos campos da fonte de dados. Também tentará deduzir o tipo de dado apropriado para a coluna, se possível. Caso contrário, o desenvolvedor precisa definir explicitamente as colunas e o mapeamento para os campos da fonte de dados.
Editable Web Components Grid
Cada operação para edição de grade inclui operações em lote, o que significa que a API oferece a opção de agrupar edições em uma única chamada de servidor, ou você pode executar operações de edição/atualização de grade conforme elas ocorrem com interações de grade. Juntamente com uma ótima experiência de desenvolvedor como uma grade editável com operações CRUD, a grade inclui navegação por teclado semelhante ao Excel. A navegação em grade padrão comum está incluída, além da opção de substituir qualquer opção de navegação para atender às necessidades de seus clientes. Uma grade editável com um ótimo esquema de navegação é fundamental para qualquer aplicativo moderno de linha de negócios, com a grade Ignite UI facilitamos.
Seguindo este tópico, você aprenderá mais sobre o modelo de célula e o modelo de edição e edição de célula.
Grid Column Configuration
IgcColumnComponenté usado para definir a coleção de colunas da grade e para habilitar recursos por coluna, como ordenação e filtragem. Modelos de célula, cabeçalho e rodapé também estão disponíveis.
Defining Columns
Vamos desligar aautoGenerate propriedade e definir a coleção de colunas na marcação:
<igc-grid id="grid1" auto-generate="false" allow-filtering="true">
<igc-column field="Name" sortable="true" header=" "></igc-column>
<igc-column field="AthleteNumber" sortable="true" header="Athlete number" filterable="false"></igc-column>
<igc-column id="trackProgress" field="TrackProgress" header="Track progress" filterable="false"></igc-column>
</igc-grid>
constructor() {
var grid1 = this.grid1 = document.getElementById('grid1') as IgcGridComponent;
grid1.data = this.data;
}
Modelo de cabeçalho
O modelo de cabeçalho pode ser definido para modificar os cabeçalhos de coluna. Os snippets abaixo mostram como formatar o texto do cabeçalho em maiúsculas.
<igc-column id="name" field="Name"></igc-column>
constructor() {
var name = this.name = document.getElementById('name') as IgcColumnComponent;
this._bind = () => {
name.headerTemplate = this.nameHeaderTemplate;
}
this._bind();
}
public nameHeaderTemplate = (ctx: IgcColumnTemplateContext) => {
return html`
${this.formatUppercase(ctx.column.field)}
`;
}
public formatUppercase(value: string) {
return value.toUpperCase();
}
Template de Célula
Quando o modelo de célula é definido, ele altera todas as células da coluna. O objeto de contexto fornecido no modelo consiste no valor da célula fornecido implicitamente e no próprio objeto de célula. Ele pode ser usado para definir um modelo onde o texto das células pode ser formatado, por exemplo, como maiúsculas e minúsculas.
<igc-column id="name" field="Name"></igc-column>
constructor() {
var name = this.name = document.getElementById('name') as IgcColumnComponent;
name.bodyTemplate = this.nameCellTemplate;
}
public nameCellTemplate = (ctx: IgcCellTemplateContext) => {
return html`
${this.formatTitleCase(ctx.implicit)}
`;
}
public formatTitleCase(value: string) {
return value.toUpperCase();
}
No trecho acima, fazemos referência ao valor da célula implicitamente fornecido. Isso é suficiente se você só quiser apresentar alguns dados e talvez aplicar algum estilo personalizado ou transformações de pipe sobre o valor da célula. No entanto, ainda mais útil é pegar aCell instância em si, como mostrado abaixo:
<igc-grid id="grid" auto-generate="false">
<igc-column id="name" field="Name" data-type="string"></igc-column>
<igc-column id="subscription" field="Subscription" data-type="boolean"></igc-column>
</igc-grid>
constructor() {
var grid = this.grid = document.getElementById('grid') as IgcGridComponent;
var name = this.name = document.getElementById('name') as IgcColumnComponent;
var subscription = this.subscription = document.getElementById('subscription') as IgcColumnComponent;
grid.data = this.data;
name.bodyTemplate = this.nameCellTemplate;
subscription.bodyTemplate = this.subscriptionCellTemplate;
}
public nameCellTemplate = (ctx: IgcCellTemplateContext) => {
return html`
<span tabindex="0" @keydown="${() => this.deleteRow(ctx.cell.id.rowIndex)}">${this.formatTitleCase(ctx.cell.value)}</span>
`;
}
public subscriptionCellTemplate = (ctx: IgcCellTemplateContext) => {
if (ctx.cell.value) {
return html` <input type="checkbox" checked /> `;
} else {
return html` <input type="checkbox"/> `;
}
}
public deleteRow(rowIndex: number) {
this.grid.deleteRow(rowIndex);
}
public formatTitleCase(value: string) {
return value.toUpperCase();
}
Nota: A grade exibe um tratamento padrão para tipos de número, string, data e colunas booleanas. Por exemplo, a coluna será exibida
checkou umcloseícone, em vez de verdadeiro/falso por padrão, para o tipo de coluna booleana.
Quando implementado corretamente, o modelo de edição de células também garante que as célulasEditValue passarão corretamente pelo ciclo de eventos de edição em grade.
Cell Editing Template
A coluna também aceita um último modelo que será usado quando uma célula estiver em modo de edição. Assim como nos outros modelos de coluna, o objeto de contexto fornecido é novamente o valor da célula e o próprio objeto célula. Claro, para tornar o modelo de edição acessível aos usuários finais, é preciso definir aeditable propriedade da coluna como true.
<igc-column id="price" field="Price" data-type="number" editable="true"></igc-column>
constructor() {
var price = this.price = document.getElementById('price') as IgcColumnComponent;
price.inlineEditorTemplate = this.priceCellTemplate;
}
public priceCellTemplate = (ctx: IgcCellTemplateContext) => {
return html`
<label>
Enter the new price tag
</label>
<input name="price" type="number" value="${ctx.cell.value}" @change="${() => this.updateValue(ctx.cell.value)}" />
`;
}
public updateValue(value: number) {
}
Certifique-se de verificar a APICell para se acostumar com as propriedades fornecidas que você pode usar nos seus templates.
Column Template API
Cada um dos modelos de coluna pode ser alterado programaticamente a qualquer momento através doIgcColumnComponent próprio objeto. Por exemplo, no código abaixo, declaramos dois modelos para nossos dados de usuário. No nosso código TypeScript, obteremos referências aos próprios templates e, com base em alguma condição, renderizaremos o template apropriado para a coluna em nossa aplicação.
<igc-grid>
<!-- Column declarations -->
</igc-grid>
var user = this.user = document.getElementById('user') as IgcColumnComponent;
// Return the appropriate template based on some condition.
// For example saved user settings, viewport size, etc.
user.bodyTemplate = this.smallView;
public normalViewTemplate = (ctx: IgcCellTemplateContext) => {
return html`
<div class="user-details">${ ctx.cell.value }</div>
<user-details-component></user-details-component>
`;
}
public smallViewTemplate = (ctx: IgcCellTemplateContext) => {
return html`
<div class="user-details-small">${ ctx.cell.value }</div>
`;
}
As propriedades das colunas também podem ser definidas no código noColumnInit evento emitido quando as colunas são inicializadas na grade.
public initColumns(column: IgcGridColumn) {
if (column.field === 'ProductName') {
column.sortable = true;
column.editable = true;
}
}
O código acima tornará a coluna ProductName classificável e editável e instanciará a interface do usuário dos recursos correspondentes (como entradas para edição etc.).
Custom Display Format
Há parâmetros opcionais para formatação:
format- determina quais partes de data/hora são exibidas, como padrão'mediumDate', equivalente a 'MMM d, y'timezone- o desfasamento do fuso horário para datas. Por padrão, usa o fuso horário local do sistema do usuário finaldigitsInfo- objetos de representação decimal. Padrão para 1.0-3
Para permitir a personalização do formato de exibição por esses parâmetros, apipeArgs entrada é exposta. Uma coluna respeitará apenas as propriedades correspondentes para seu tipo de dado, sepipeArgs for definido. Exemplo:
<igc-column id="orderDate" field="OrderDate" data-type="date"></igc-column>
private _columnPipeArgs: any | null = null;
public get columnPipeArgs(): any {
if (this._columnPipeArgs == null)
{
var columnPipeArgs: any = {};
columnPipeArgs.format = "longDate";
columnPipeArgs.timezone = "UTC";
columnPipeArgs.digitsInfo = "1.2-2"
this._columnPipeArgs = columnPipeArgs;
}
return this._columnPipeArgs;
}
constructor() {
var orderDate = this.orderDate = document.getElementById('orderDate') as IgcColumnComponent;
orderDate.pipeArgs = this.columnPipeArgs;
}
AOrderDate coluna respeitará apenas asformat propriedades etimezone e respeitará.UnitPricedigitsInfo
Todos os tipos de dados de coluna disponíveis podem ser encontrados no tópico oficial Tipos de coluna.
Grid Data Structure
EleIgcGridComponent lida com dados planos e POJO aninhados (objetos Java comuns). A estrutura de dados específica para renderização está na forma:
const OBJECT_ARRAY = [{
ObjectKey1: value1,
ObjectKey2: value2,
// ...
ObjectKeyN: valueN
},
// ...
}];
const POJO = [{
ObjectKey1: value1,
ObjectKey2: value2,
// ...
ObjectKeyN: {
ObjectKeyN1: value1,
ObjectKeyN2: value2,
// ...
ObjectKeyNM: valueNM,
}
},
// ...
}];
AVISO: Os valores de chave não devem conter matrizes.
Se você usar
autoGenerate colunas, as chaves de dados devem ser idênticas.
Grid Data Binding
Nosso Web Components Data Grid oferece opções de vinculação de dados incomparáveis e é otimizado para atualizações em tempo real e rolagem suave. Com renderização de baixa latência, a grade garante que qualquer alteração na interface do usuário seja exibida em um instante, incluindo dados de transmissão ao vivo, grandes conjuntos de dados e muito mais.
Antes de prosseguir com o Web Components Data Grid, queremos alterar a grade para se vincular ao serviço de dados remoto, que é o cenário comum em aplicativos de grande escala.
Você pode fazer isso pegando os dados de uma determinada URL que recebe uma resposta JSON e atribuindo-os à propriedade dadata grade usada como fonte de dados da grade:
<igc-grid id="grid1"></igc-grid>
public fetchData(url: string): void {
fetch(url)
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => this.onDataLoaded(data));
}
public onDataLoaded(jsonData: any[]) {
var grid1 = document.getElementById("grid1") as IgcGridComponent;
grid1.data = jsonData;
}
Nota: A propriedade de gradeautoGenerate é melhor evitar ao vincular dados remotos por enquanto. Ele assume que os dados estão disponíveis para inspecioná-los e gerar as colunas apropriadas. Isso geralmente não acontece até que o serviço remoto responda, e a grade gera um erro. DisponibilizarautoGenerate, quando vinculado ao serviço remoto, está no nosso roteiro para versões futuras.
Complex Data Binding
A vinculação de dados complexos permite uma interação perfeita com dados de vários níveis, conjuntos de dados complexos do mundo real, módulos de dados orientados a objetos, etc. Usando nosso Web Components Data Grid, você pode facilmente associar a objetos complexos (incluindo estruturas de dados que se aninham mais profundamente do que um nível). Isso acontece por meio de um caminho de propriedades no registro de dados.
Dê uma olhada no seguinte modelo de dados:
interface AminoAcid {
name: string;
abbreviation: {
short: string;
long: string;
}
weight: {
molecular: number;
residue: number;
},
formula: {
molecular: string;
residue: string;
}
}
Por exemplo, para exibir os pesos de um determinado aminoácido na grade, o seguinte trecho será suficiente
<igc-column field="weight.molecular"></igc-column>
<igc-column field="weight.residue"></igc-column>
Uma forma alternativa de vincular dados complexos, ou de visualizar dados compostos (de mais de uma coluna) noIgcGridComponent é usar um modelo personalizado de corpo para a coluna. Geralmente, pode-se:
- use o
valueda célula, que contém os dados aninhados
- use o
cellobjeto no template, a partir do qual acessar octx.cell.id.rowIndexouctx.cell.id.rowIDobter a linha via API da grade e recuperar qualquer valor dela e interpolar esses no template.
<igc-column id="abbreviationLong" field="abbreviation.long"></igc-column>
constructor() {
var grid = (this.grid = document.getElementById("grid") as IgcGridComponent);
var abbreviationLong = this.abbreviationLong = document.getElementById('abbreviationLong') as IgcColumnComponent;
abbreviationLong.bodyTemplate = this.abbreviationLongCellTemplate;
}
public abbreviationLongCellTemplate = (ctx: IgcCellTemplateContext) => {
return html`
<div>
<div>
${ ctx.cell.value }
${this.getName(ctx.cell.id.rowIndex)}
${this.getWeight(ctx.cell.id.rowIndex)}
</div>
</div>
`;
}
public getName(rowIndex: number) {
return this.grid.getRowByIndex(rowIndex).data["Name"];
}
public getWeight(rowIndex: number) {
return this.grid.getRowByIndex(rowIndex).data["weight"]["molecular"];
}
Aqui está um exemplo de como o modelo de corpo é usado para exibir dados complexos. Abaixo estão os dados que vamos usar:
export const EMPLOYEE_DATA = [
{
Age: 55,
Employees: [
{
Age: 43,
HireDate: new Date(2011, 6, 3),
ID: 3,
Name: "Michael Burke",
Title: "Senior Software Developer"
},
{
Age: 29,
HireDate: new Date(2009, 6, 19),
ID: 2,
Name: "Thomas Anderson",
Title: "Senior Software Developer"
},
{
Age: 31,
HireDate: new Date(2014, 8, 18),
ID: 11,
Name: "Monica Reyes",
Title: "Software Development Team Lead"
},
{
Age: 35,
HireDate: new Date(2015, 9, 17),
ID: 6,
Name: "Roland Mendel",
Title: "Senior Software Developer"
}],
HireDate: new Date(2008, 3, 20),
ID: 1,
Name: "John Winchester",
Title: "Development Manager"
}
]
O modelo personalizado para a coluna, que renderizará os dados aninhados:
<igc-column id="employees" field="Employees" header="Employees" width="40%"></igc-column>
constructor() {
var employees = this.employees = document.getElementById('employees') as IgcColumnComponent;
employees.bodyTemplate = this.addressCellTemplate;
}
public addressCellTemplate = (ctx: IgcCellTemplateContext) => {
return html`
<igc-expansion-panel>
<div slot="title" style="font-size: 1.1em; font-weight: bold; margin-top: 1rem; margin-bottom: 0.25rem;">
${ctx.cell.value[0].Name}
</div>
<div class="description">
<div style="display: flex; align-items: center;">
<div for="title" style="width: 2rem; margin: 0rem;">Title</div>
<input id='Title' type="text" name="title" value="${ctx.cell.value[0].Title}" style="text-overflow: ellipsis;" />
</div>
<div style="display: flex; align-items: center;">
<div for="age" style="width: 2rem; margin: 0rem;">Age</div>
<input id='Age' type="text" name="title" value="${ctx.cell.value[0].Age}" style="text-overflow: ellipsis;" />
</div>
</div>
</igc-expansion-panel>
`;
}
E o resultado dessa configuração é:
Working with Flat Data Overview
A abordagem de ligação de dados planos é semelhante à que já descrevemos acima, mas em vez do valor da célula, vamos usar adata propriedade de oIgcGridRowComponent.
Como a grade de Web Components é um componente para renderização, manipulação e preservação de registros de dados, ter acesso a cada registro de dados oferece a oportunidade de personalizar a abordagem de manuseamento deles. Odata imóvel oferece essa oportunidade.
Abaixo estão os dados que vamos usar:
export const DATA: any[] = [
{
Address: "Obere Str. 57",
City: "Berlin",
CompanyName: "Alfreds Futterkiste",
ContactName: "Maria Anders",
ContactTitle: "Sales Representative",
Country: "Germany",
Fax: "030-0076545",
ID: "ALFKI",
Phone: "030-0074321",
PostalCode: "12209",
Region: null
}
]
O modelo personalizado:
<igc-column id="address" field="Address" header="Address" width="25%" editable="true"></igc-column>
constructor() {
var address = this.address = document.getElementById('address') as IgcColumnComponent;
address.bodyTemplate = this.addressCellTemplate;
}
public addressCellTemplate = (ctx: IgcCellTemplateContext) => {
return html`
<div class="address-container">
<!-- In the Address column combine the Country, City and PostCode values of the corresponding data record -->
<span><strong>Country:</strong> ${this.getCountry(ctx.cell.id.rowIndex)}</span>
<br/>
<span><strong>City:</strong> ${this.getCity(ctx.cell.id.rowIndex)}</span>
<br/>
<span><strong>Postal Code:</strong> ${this.getPostalCode(ctx.cell.id.rowIndex)}</span>
</div>
`;
}
public getCountry(rowIndex: number) {
return this.grid.getRowByIndex(rowIndex).data["Country"];
}
public getCity(rowIndex: number) {
return this.grid.getRowByIndex(rowIndex).data["City"];
}
public getPostalCode(rowIndex: number) {
return this.grid.getRowByIndex(rowIndex).data["PostalCode"];
}
Lembre-se de que, com o modelo definido acima, você não poderá fazer operações de edição, portanto, precisamos de um modelo de editor.
<igc-column id="address" field="Address" data-type="number" width="25%" editable="true"></igc-column>
constructor() {
var address = this.address = document.getElementById('address') as IgcColumnComponent;
address.inlineEditorTemplate = this.webGridCompositeAddressEditCellTemplate;
}
public webGridCompositeAddressEditCellTemplate = (ctx: IgcCellTemplateContext) => {
var cell = ctx.cell as any;
if (cell === undefined || cell.row === undefined || cell.row.data === undefined) {
return html``
}
function keyUpHandler(event: any, ctx: IgcCellTemplateContext) {
var cell = ctx.cell as any;
if (cell !== undefined && cell.row !== undefined && cell.row.data !== undefined) {
cell.row.data[event.target.id] = event.target.value;
}
}
return html`<div class="address-container--edit" style="display: inline-grid">
<div>
<span><strong>Country:</strong></span>
<input id='Country' @keyup=${(e: any) => keyUpHandler(e, ctx)} value="${cell.row.data.Country}"></input>
<br>
<span><strong>City:</strong></span>
<input id='City' @keyup=${(e: any) => keyUpHandler(e, ctx)} value="${cell.row.data.City}"></input>
</div>
<div>
<span><strong>Postal Code:</strong></span>
<input id='PostalCode' @keyup=${(e: any) => keyUpHandler(e, ctx)} value="${cell.row.data.PostalCode}"></input>
<br>
<span><strong>Selected:</strong></span>
<input id='Phone' @keyup=${(e: any) => keyUpHandler(e, ctx)} value="${cell.row.data.Phone}"></input>
</div>
<br>
</div>`;
}
Working with Flat Data Example
Usar trechos de código da seção anterior resultará no seguinte exemplo deIgcGridComponent
Keyboard Navigation
A navegaçãoIgcGridComponent por teclado oferece uma rica variedade de interações com o teclado para o usuário. Ele melhora a acessibilidade e permite uma navegação intuitiva por qualquer tipo de elemento interno (célula, linha, cabeçalho de coluna, barra de ferramentas, rodapé, etc.).
Styling Web Components Grid
Nota: A grade usa o layout de grade css, que não é suportado no IE sem prefixação, conseqüentemente não será renderizado corretamente.
Além dos temas predefinidos, a grade pode ser personalizada ainda mais definindo algumas das propriedades CSS disponíveis. Caso você queira alterar o plano de fundo do cabeçalho e a cor do texto, você precisa definir uma classe para a grade primeiro:
<igc-grid class="grid"></igc-grid>
Depois, defina as--header-background propriedades e--header-text-color CSS para essa classe:
.grid {
--header-background: #494949;
--header-text-color: #FFF;
}
Known Limitations
| Limitação | Descrição |
|---|---|
As larguras das colunas definidas empercentage epx |
Atualmente, não oferecemos suporte à mistura de larguras de coluna com% epx. |
Ao tentar filtrar uma coluna do tiponumber |
Se um valor diferente do inseridonumber na entradaNaN de filtragem for retornado devido a uma conversão incorreta. |
A gradewidth não depende das larguras das colunas |
Owidth de todas as colunas não determina a abrangência da grade em si. Ele é determinado pelas dimensões do contêiner pai ou pela grade definida.width |
| Grade aninhada no contêiner pai | Quando awidth grade não está definida e é colocada em um contêiner pai com dimensões definidas, a grade se estende até esse contêiner. |
As colunas têm uma largura mínima permitida. Dependendo da--ig-size variável CSS, eles são os seguintes:"pequeno": 56px "médio": 64px "grande": 80px |
Se a largura for menor que o mínimo permitido for definida, isso não afetará os elementos renderizados. Eles serão renderizados com a largura mínima permitida para o correspondente--ig-size. Isso pode levar a um comportamento inesperado com a virtualização horizontal e, portanto, não é suportado. |
| A altura da linha não é afetada pela altura das células que não estão renderizadas no momento. | Devido à virtualização, uma coluna com um modelo personalizado (que altera a altura da célula) que não está no modo de exibição não afetará a altura da linha. A altura da linha será afetada somente enquanto a coluna relacionada for rolada na exibição. |
API References
IgcGridComponentIgcColumnComponentCellIgcCellTemplateContextIgcGridRowComponentIgcGridToolbarComponentIgcPaginatorComponent
Additional Resources
Nossa comunidade é ativa e sempre acolhedora para novas ideias.